.jpg?auto=compress,webp&upscale=true&width=610&height=488&name=shutterstock_2446979289%20(1).jpg)
I started writing this blog post the day after I came home from KubeCon and CloudNativeCon 2022. The main thing I noticed was that the content of the talks has changed over the last few years.
Kubernetes’ new challenges
When looking at the topics of this year’s KubeCon / CloudNativeCon, it feels like a lot of questions about Kubernetes, types of cloud, logging tools and more are answered for most companies. This makes sense, because more and more organizations have already successfully adopted Kubernetes. Kubernetes is no longer considered the next big thing, but rather the logical choice. However, we’ve noticed (during the talks, but also in our own journey) that new problems and challenges have arisen, leading to other questions:
- How can I implement more automation?
- How can I control/lower the costs for these setups?
- Is there a way to expand on whatever exists and add my own functionalities to Kubernetes?
One of the possible ways to add functionalities to Kubernetes is using Operators. In this blog post, I will briefly explain how Operators work.
How Operators work
The concept of an operator is quite simple. I believe the easiest way to explain it is by actually installing an operator.
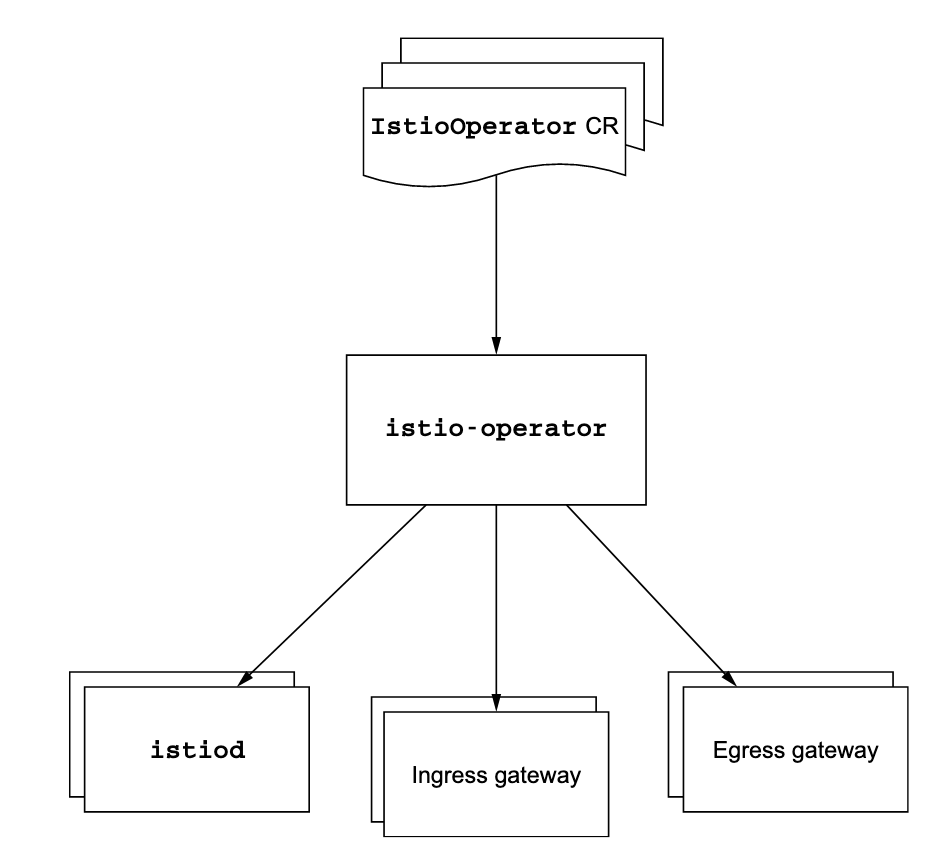
Within ACA, we use the istio operator. The exact steps of installing depends on the operator you are installing, but usually they’re quite similar.
First, install the istioctl binary on the machine that has access to the Kubernetes api. The next step is to run the command to install the operator.
curl -sL https://istio.io/downloadIstioctl | sh -
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.istioctl/bin
istioctl operator initThis will create the operator resource(s) in the istio-system namespace. You should see a pod running.
kubectl get pods -n istio-operator
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
istio-operator istio-operator-564d46ffb7-nrw2t 1/1 Running 0 20s
kubectl get crd
NAME CREATED AT
istiooperators.install.istio.io 2022-05-21T19:19:43ZAs you can see, a new CustomResourceDefinition called istiooperators.install.istio.io is created. This is a blueprint that specifies how resource definitions should be added to the cluster. To create config, we need to know what ‘kind’ of config the CRD expects to be created.
kubectl get crd istiooperators.install.istio.io -oyaml
…
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: IstioOperator
…Let’s create a simple config file.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:
namespace: istio-system
name: istio-controlplane
spec:
profile: minimal
EOFOnce the ResourceDefinition that contains the configuration is added to the cluster, the operator will make sure the resources in the cluster match whatever is defined in the configuration. You’ll see that new resources are created.
kubectl get pods -A
istio-system istiod-7dc88f87f4-rsc42 0/1 Pending 0 2m27sSince I run a small kind cluster, the istiod pod can’t be scheduled and is stuck in a Pending state. Let me explain the process first before changing this.
The istio-operator will keep watching the IstioOperator configuration file for changes. If changes are made to the file, it will only make the changes that are required to update the resources in the cluster to match the state specified in the configuration file. This behavior is called reconciliation.
Let’s watch the IstioOperator configuration file status. Note that it’s created in the istio-system namespace.
kubectl get istiooperator -n istio-system
NAME REVISION STATUS AGE
istio-controlplane RECONCILING 3mAs you can see, this is still reconciling, because the pod can’t start. After some time, it’ll go in an ERROR state.
kubectl get istiooperator -n istio-system
NAME REVISION STATUS AGE
istio-controlplane ERROR 6m58sYou can also check the istio-operator log for useful information.
kubectl -n istio-operator logs istio-operator-564d46ffb7-nrw2t --tail 20
- Processing resources for Istiod.
- Processing resources for Istiod. Waiting for Deployment/istio-system/istiod
✘ Istiod encountered an error: failed to wait for resource: resources not ready after 5m0s: timed out waiting for the condition.
Since I’m running a small demo cluster, I’ll update the memory limit so the POD can be scheduled. This is done within the spec: part of the IstioOperator definition.
kubectl -n istio-system edit istiooperator istio-controlplane
spec:
profile: minimal
components:
pilot:
k8s:
resources:
requests:
memory: 128Mi
The istiooperator will go back to a RECONCILING state.
kubectl get istiooperator -n istio-system
NAME REVISION STATUS AGE
istio-controlplane RECONCILING 11mAnd after some time, it becomes HEALTHY.
kubectl get istiooperator -n istio-system
NAME REVISION STATUS AGE
istio-controlplane HEALTHY 12mYou can see the istiod pod is running.
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS
istio-system istiod-7dc88f87f4-n86z9 1/1 RunningApart from the istiod deployment, a lot of new CRDs are added as well.
authorizationpolicies.security.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
destinationrules.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
envoyfilters.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
gateways.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
istiooperators.install.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:07:01Z
peerauthentications.security.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
proxyconfigs.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
requestauthentications.security.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
serviceentries.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
sidecars.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
telemetries.telemetry.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
virtualservices.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:05Z
wasmplugins.extensions.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:06Z
workloadentries.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:06Z
workloadgroups.networking.istio.io 2022-05-21T20:08:06ZHow the operator works - summary
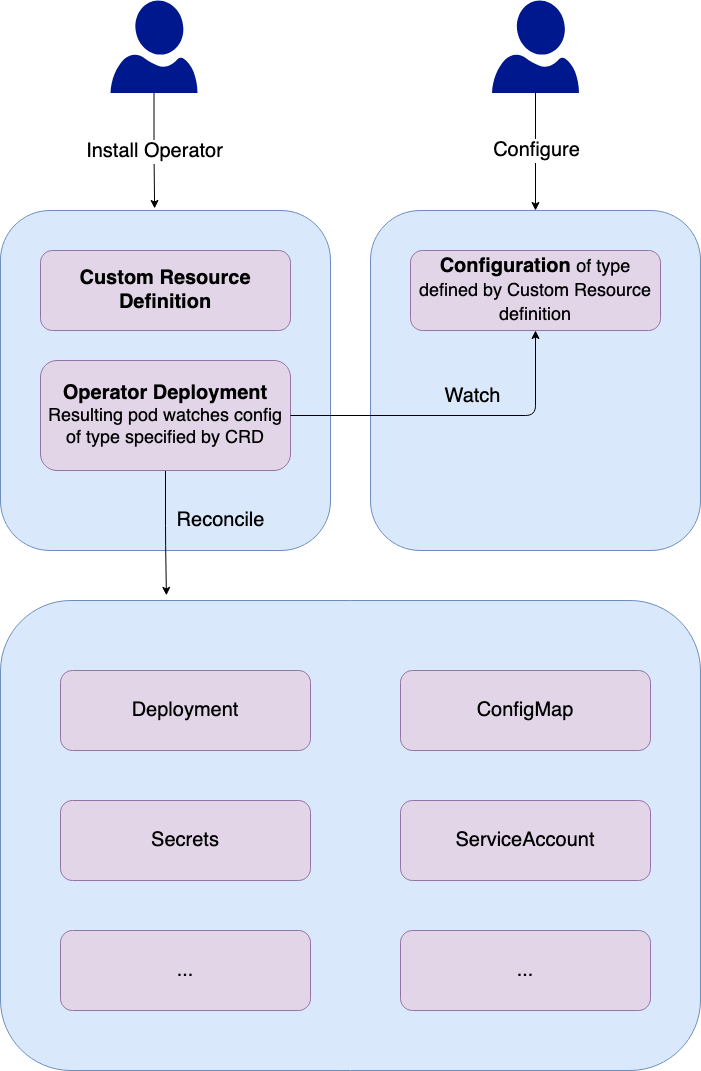
As you can see, this is a very easy way to quickly set up istio within our cluster. In short, these are the steps:
- Install the operator
- One (or more) CustomResourceDefinitions is added that provides a blueprint for the objects that can be created/managed. A deployment is created, which in turn creates a Pod that monitors the Configurations of the kinds that are specified by the CRD.
- The user adds configuration to the cluster, with its type specified by the CRD.
- The operator POD notices the new configuration and takes all steps that are required to make sure the cluster is in the desired state specified by the configuration.
Benefits of the operator approach
The operator approach makes it easy to package a set of resources like Deployments, Jobs, CustomResourceDefinitions. This way, it’s easy to add additional behavior and capabilities to Kubernetes.
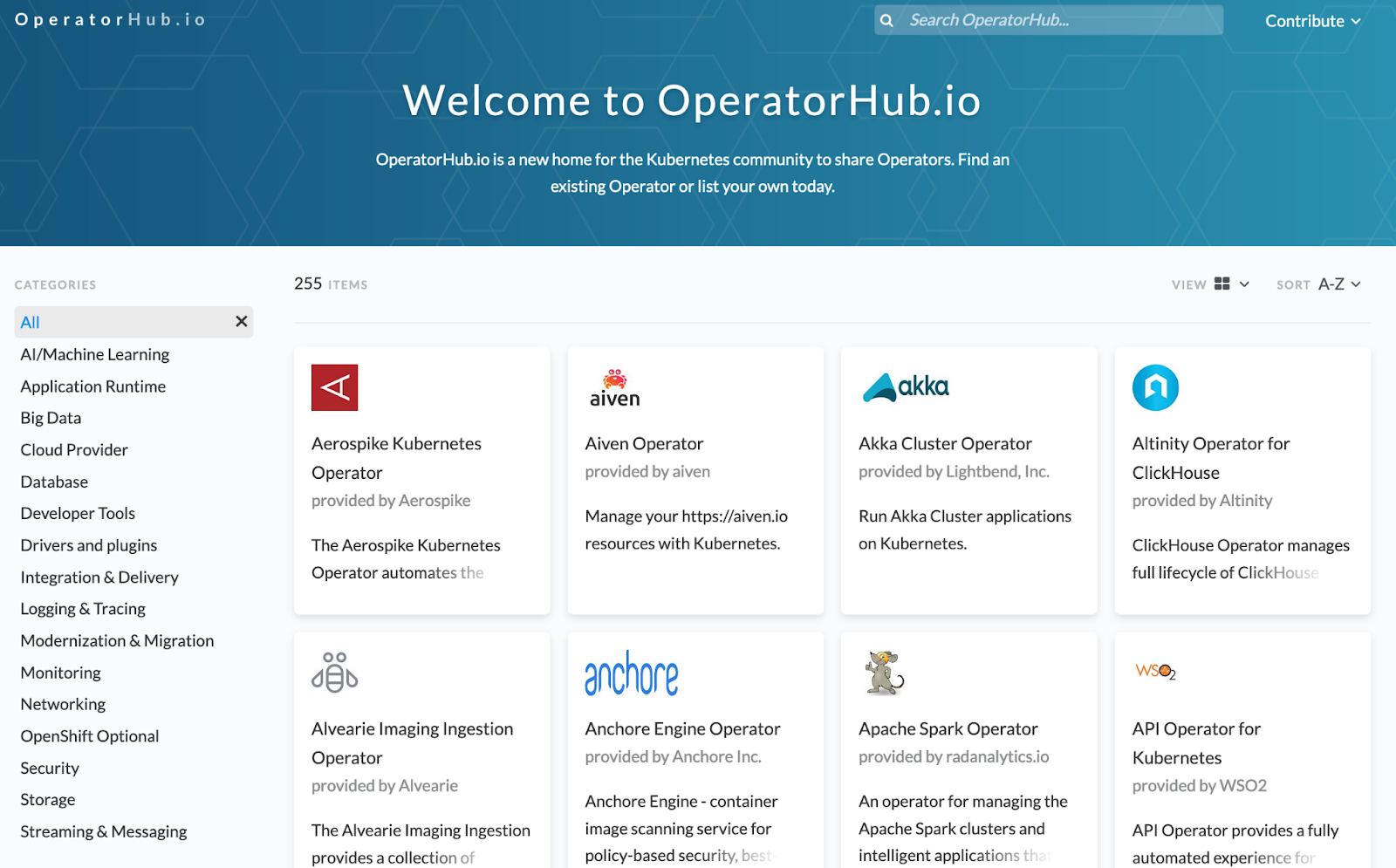
There’s a library which lists the available operators which can be found at https://operatorhub.io/, counting 255 operators at the moment of writing. The operators are usually installed with just a few commands or lines of code.
It’s also possible to create your own operators. It might make sense to package a set of deployments, jobs, CRDs, … that provide a specific functionality as an operator. The operator can be handled as operators and use pipelines for CVE validations, E2E tests, rollout to test environments, and more before a new version is promoted to production.
Pitfalls
We have been using Kubernetes for a long time within the ACA Group and have collected some security best-practices during this period. We’ve noticed that one-file-deployments and helm charts from the internet are usually not as well configured as we want them to be. Think about RBAC rules that give too many permissions, resources not currently namespaced or containers running as root.
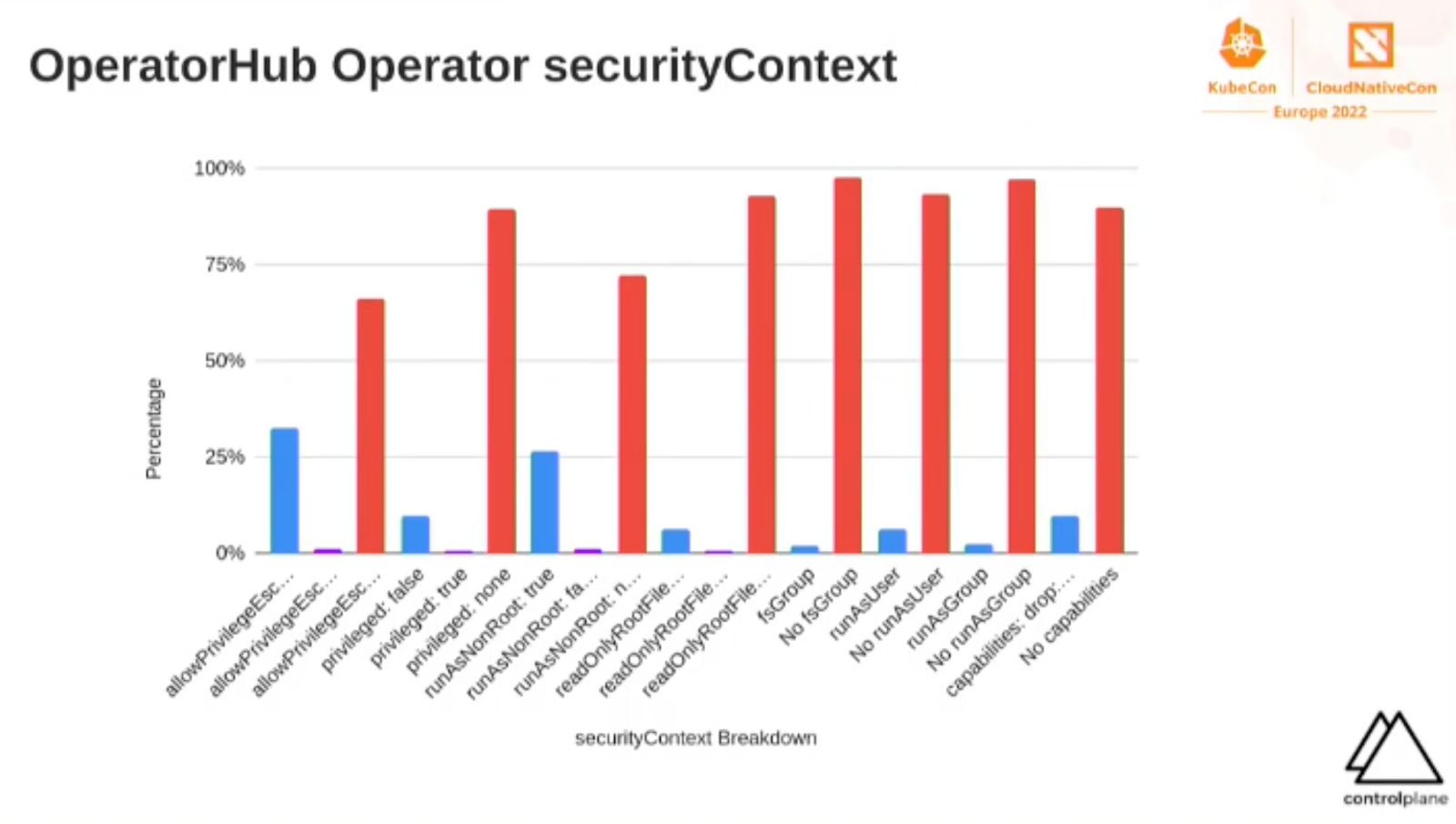
When using operators from operatorhub.io, you basically trust the vendor or provider to follow security best-practices. However … one of the talks at KubeCon 2022 that made the biggest impression on me, stated that a lot of the operators have issues regarding security. I would suggest you to watch Tweezering Kubernetes Resources: Operating on Operators - Kevin Ward, ControlPlane before installing.
Another thing we’ve noticed is that using operators can speed up the process to implement new tools and features. Be sure to read the documentation that was provided by the creator of an operator before you dive into advanced configuration. It might be possible that not all features are actually implemented on the CRD that is created by the operator. However, it is bad practice to directly manipulate the resources that were created by the operator. The operator is not tested against your manual changes and this might cause inconsistencies. Additionally, new operator versions might (partly) undo your changes, which also might cause problems.
At that point, you’re basically stuck, unless you create your own operator that provides additional features. We’ve also noticed that there is no real ‘rule book’ on how to provide CRDs and documentation is not always easy to find or understand.
Conclusion
Operators are currently a hot topic within the Kubernetes community. The number of available operators is growing fast, making it easy to add functionality to your cluster. However, there is no rule book or a minimal baseline of quality. When installing operators from the operatorhub, be sure to check the contents or validate the created resources on a local setup. We expect to see some changes and improvements in the near future, but at this point they can be very useful already.



What others have also read


In the complex world of modern software development, companies are faced with the challenge of seamlessly integrating diverse applications developed and managed by different teams. An invaluable asset in overcoming this challenge is the Service Mesh. In this blog article, we delve into Istio Service Mesh and explore why investing in a Service Mesh like Istio is a smart move." What is Service Mesh? A service mesh is a software layer responsible for all communication between applications, referred to as services in this context. It introduces new functionalities to manage the interaction between services, such as monitoring, logging, tracing, and traffic control. A service mesh operates independently of the code of each individual service, enabling it to operate across network boundaries and collaborate with various management systems. Thanks to a service mesh, developers can focus on building application features without worrying about the complexity of the underlying communication infrastructure. Istio Service Mesh in Practice Consider managing a large cluster that runs multiple applications developed and maintained by different teams, each with diverse dependencies like ElasticSearch or Kafka. Over time, this results in a complex ecosystem of applications and containers, overseen by various teams. The environment becomes so intricate that administrators find it increasingly difficult to maintain a clear overview. This leads to a series of pertinent questions: What is the architecture like? Which applications interact with each other? How is the traffic managed? Moreover, there are specific challenges that must be addressed for each individual application: Handling login processes Implementing robust security measures Managing network traffic directed towards the application ... A Service Mesh, such as Istio, offers a solution to these challenges. Istio acts as a proxy between the various applications (services) in the cluster, with each request passing through a component of Istio. How Does Istio Service Mesh Work? Istio introduces a sidecar proxy for each service in the microservices ecosystem. This sidecar proxy manages all incoming and outgoing traffic for the service. Additionally, Istio adds components that handle the incoming and outgoing traffic of the cluster. Istio's control plane enables you to define policies for traffic management, security, and monitoring, which are then applied to the added components. For a deeper understanding of Istio Service Mesh functionality, our blog article, "Installing Istio Service Mesh: A Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide" , provides a detailed, step-by-step explanation of the installation and utilization of Istio. Why Istio Service Mesh? Traffic Management: Istio enables detailed traffic management, allowing developers to easily route, distribute, and control traffic between different versions of their services. Security: Istio provides a robust security layer with features such as traffic encryption using its own certificates, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), and capabilities for implementing authentication and authorization policies. Observability: Through built-in instrumentation, Istio offers deep observability with tools for monitoring, logging, and distributed tracing. This allows IT teams to analyze the performance of services and quickly detect issues. Simplified Communication: Istio removes the complexity of service communication from application developers, allowing them to focus on building application features. Is Istio Suitable for Your Setup? While the benefits are clear, it is essential to consider whether the additional complexity of Istio aligns with your specific setup. Firstly, a sidecar container is required for each deployed service, potentially leading to undesired memory and CPU overhead. Additionally, your team may lack the specialized knowledge required for Istio. If you are considering the adoption of Istio Service Mesh, seek guidance from specialists with expertise. Feel free to ask our experts for assistance. More Information about Istio Istio Service Mesh is a technological game-changer for IT professionals aiming for advanced control, security, and observability in their microservices architecture. Istio simplifies and secures communication between services, allowing IT teams to focus on building reliable and scalable applications. Need quick answers to all your questions about Istio Service Mesh? Contact our experts
Read more

On December 7 and 8, 2023, several ACA members participated in CloudBrew 2023 , an inspiring two-day conference about Microsoft Azure. In the scenery of the former Lamot brewery, visitors had the opportunity to delve into the latest cloud developments and expand their network. With various tracks and fascinating speakers, CloudBrew offered a wealth of information. The intimate setting allowed participants to make direct contact with both local and international experts. In this article we would like to highlight some of the most inspiring talks from this two-day cloud gathering: Azure Architecture: Choosing wisely Rik Hepworth , Chief Consulting Officer at Black Marble and Microsoft Azure MVP/RD, used a customer example in which .NET developers were responsible for managing the Azure infrastructure. He engaged the audience in an interactive discussion to choose the best technologies. He further emphasized the importance of a balanced approach, combining new knowledge with existing solutions for effective management and development of the architecture. From closed platform to Landing Zone with Azure Policy David de Hoop , Special Agent at Team Rockstars IT, talked about the Azure Enterprise Scale Architecture, a template provided by Microsoft that supports companies in setting up a scalable, secure and manageable cloud infrastructure. The template provides guidance for designing a cloud infrastructure that is customizable to a business's needs. A critical aspect of this architecture is the landing zone, an environment that adheres to design principles and supports all application portfolios. It uses subscriptions to isolate and scale application and platform resources. Azure Policy provides a set of guidelines to open up Azure infrastructure to an enterprise without sacrificing security or management. This gives engineers more freedom in their Azure environment, while security features are automatically enforced at the tenant level and even application-specific settings. This provides a balanced approach to ensure both flexibility and security, without the need for separate tools or technologies. Belgium's biggest Azure mistakes I want you to learn from! During this session, Toon Vanhoutte , Azure Solution Architect and Microsoft Azure MVP, presented the most common errors and human mistakes, based on the experiences of more than 100 Azure engineers. Using valuable practical examples, he not only illustrated the errors themselves, but also offered clear solutions and preventive measures to avoid similar incidents in the future. His valuable insights helped both novice and experienced Azure engineers sharpen their knowledge and optimize their implementations. Protecting critical ICS SCADA infrastructure with Microsoft Defender This presentation by Microsoft MVP/RD, Maarten Goet , focused on the use of Microsoft Defender for ICS SCADA infrastructure in the energy sector. The speaker shared insights on the importance of cybersecurity in this critical sector, and illustrated this with a demo demonstrating the vulnerabilities of such systems. He emphasized the need for proactive security measures and highlighted Microsoft Defender as a powerful tool for protecting ICS SCADA systems. Using Azure Digital Twin in Manufacturing Steven De Lausnay , Specialist Lead Data Architecture and IoT Architect, introduced Azure Digital Twin as an advanced technology to create digital replicas of physical environments. By providing insight into the process behind Azure Digital Twin, he showed how organizations in production environments can leverage this technology. He emphasized the value of Azure Digital Twin for modeling, monitoring and optimizing complex systems. This technology can play a crucial role in improving operational efficiency and making data-driven decisions in various industrial applications. Turning Azure Platform recommendations into gold Magnus Mårtensson , CEO of Loftysoft and Microsoft Azure MVP/RD, had the honor of closing CloudBrew 2023 with a compelling summary of the highlights. With his entertaining presentation he offered valuable reflection on the various themes discussed during the event. It was a perfect ending to an extremely successful conference and gave every participant the desire to immediately put the insights gained into practice. We are already looking forward to CloudBrew 2024! 🚀
Read more

Like every year, Amazon held its AWS re:Invent 2021 in Las Vegas. While we weren’t able to attend in person due to the pandemic, as an AWS Partner we were eager to follow the digital event. Below is a quick rundown of our highlights of the event to give you a summary in case you missed it! AWS closer to home AWS will build 30 new ‘ Local Zones ’ in 2022, including one in our home base: Belgium. AWS Local Zones are a type of infrastructure deployment that places compute, storage, database, and other select AWS services close to large population and industry centers. The Belgian Local Zone should be operational by 2023. Additionally, the possibilities of AWS Outposts have increased . The most important change is that you can now run far more services on your own server delivered by AWS. Quick recap: AWS Outposts is a family of fully managed solutions delivering AWS infrastructure and services to virtually any on-premises or edge location for a consistent hybrid experience. Outposts was previously only available in a 42U Outposts rack configuration. From now on, AWS offers a variety of form factors, including 1U and 2U Outposts servers for when there’s less space available. We’re very tempted to get one for the office… AWS EKS Anywhere was previously announced, but is now a reality! With this service, it’s possible to set up a Kubernetes cluster on your own infrastructure or infrastructure from your favorite cloud provider, while still managing it through AWS EKS. All the benefits of freedom of choice combined with the unified overview and dashboard of AWS EKS. Who said you can’t have your cake and eat it too? Low-code to regain primary focus With Amplify Studio , AWS takes the next step in low-code development. Amplify Studio is a fully-fledged low-code generator platform that builds upon the existing Amplify framework. The platform allows users to build applications through drag and drop with the possibility of adding custom code wherever necessary. Definitely something we’ll be looking at on our next Ship-IT Day! Machine Learning going strong(er) Ever wanted to start with machine learning, but not quite ready to invest some of your hard-earned money? With SageMaker Studio Lab , AWS announced a free platform that lets users start exploring AI/ML tools without having to register for an AWS account or leave credit card details behind. You can try it yourself for free in your browser through Jupyter notebooks ! Additionally, AWS announced SageMaker Canvas : a visual, no-code machine learning capability for business analysts. This allows them to get started with ML without having extensive experience and get more insights in data. The third chapter in the SageMaker saga consists of SageMaker Ground Truth Plus . With this new service, you hire a team of experts to train and label your data, a traditionally very labor intensive process. According to Amazon, customers can expect to save up to 40% through SageMaker Ground Truth Plus. There were two more minor announcements: the AI ML Scholarschip Program , a free program for students to get to know ML tools, and Lex Automated Chatbot Designer , which lets you quickly develop a smart chatbot with advanced natural language processing support. Networking for everyone Tired of less than optimal reception or a slow connection? Why not build your own private 5G network? Yep: with AWS Private 5G , Amazon delivers the hardware, management and sim cards for you to set up your very own 5G network. Use cases (besides being fed up with your current cellular network) include warehouses or large sites (e.g. a football stadium) that require low latency, excellent coverage and a large bandwidth. The best part? Customers only pay for the end user’s usage of the network. Continuing the network theme, there’s now AWS Cloud WAN . This service allows users to build a managed WAN (Wide Area Network) to connect cloud and on-premise environments with a central management UI on a network components level as well as service level. Lastly, there’s also AWS Workspaces Web . Through this service, customers can grant employees safe access to internal website and SaaS applications. The big advantage here is that information critical to the company never leaves the environment and doesn’t leave any traces on workstations, thanks to a non-persistent web browser. Kubernetes anyone? No AWS event goes without mentioning Kubernetes, and AWS re:Invent 2021 is no different. Amazon announced two new services in the Kubernetes space: AWS Karpenter and AWS Marketplace for Containers Anywhere . With AWS Karpenter, managing autoscaling Kubernetes infrastructure becomes both simpler and less restrictive. It takes care of automatically starting compute when the load of an application changes. Interestingly, Karpenter is fully open-source, a trend which we’ll see more and more according to Amazon. AwS Marketplace for Containers Anywhere is primarily useful for customers who’ve already fully committed to container managed platforms. It allows users to search, subscribe and deploy 3rd party Kubernetes apps from the AWS Marketplace in any Kubernetes cluster, no matter the environment. IoT updates There have been numerous smaller updates to AWS’s IoT services, most notably to: GreenGrass SSM , which now allows you to securely manage your devices using AWS Systems Manager Amazon Monitron to predict when maintenance is required for rotating parts in machines AWS IoT TwinMaker , to simply make Digital Twins of real-world systems AWS IoT FleetWise , whichs helps users to collect vehicle data in the cloud in near-real time. Upping the serverless game In the serverless landscape, AWS announced serverless Redshift , EMR , MSK , and Kinesis . This enables to set up services while the right instance type is automatically linked. If the service is not in use, the instance automatically stops. This way, customers only pay for when a service is actually being used. This is particularly interesting for experimental services and integrations in environments which do not get used very often. Sustainability Just like ACA Group’s commitment to sustainability , AWS is serious about their ambition towards net-zero carbon by 2040. They’ve developed the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint tool, which lets users calculate carbon emissions through their website . Other announcements included AWS Mainframe Modernization , a collection of tools and guides to take over existing mainframes with AWS, and AWS Well-Architected Framework , a set of design principles, guidelines, best practices and improvements to validate sustainability goals and create reports. We can't wait to start experimenting with all the new additions and improvements announced at AWS re:Invent 2021. Thanks for reading! Discover our cloud hosting services
Read moreWant to dive deeper into this topic?
Get in touch with our experts today. They are happy to help!

Want to dive deeper into this topic?
Get in touch with our experts today. They are happy to help!

Want to dive deeper into this topic?
Get in touch with our experts today. They are happy to help!

Want to dive deeper into this topic?
Get in touch with our experts today. They are happy to help!


